Aniline, also known as aminobenzene, with molecular formula C6H7N, is a colorless oily liquid, decomposed by heating to 370℃. Slightly soluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol, ether and other organic solvents.

Aniline is one of the most important amine substances.
It is mainly used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs, resins, and also used as rubber vulcanization accelerator, etc..
It can also be used as a black dye by itself.
Its derivative methyl orange is used as an indicator for acid-base titrations.
On October 27, 2017, the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer published a preliminary compilation of references to the list of carcinogens, and aniline is in the list of carcinogens in category 3.
1.Introduction of aniline
Aniline, also known as aminobenzene, molecular formula: C6H7N.
colorless oily liquid. Slightly soluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol, ether and other organic solvents. Aniline is one of the most important amine substances.
It is mainly used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs, resins and also used as rubber vulcanization accelerator.
It can also be used as a black dye by itself. Its derivative methyl orange can be used as an indicator for acid-base titration.
Chemical properties
It is alkaline and can be combined with hydrochloric acid to form hydrochloride and with sulfuric acid to form sulfate.
It can act as halogenation, acetylation, diazotization, etc.
Flammable when exposed to open flame and high heat, the flame of combustion will produce smoke. Strong reaction with acids, halogens, alcohols and amines will cause combustion.
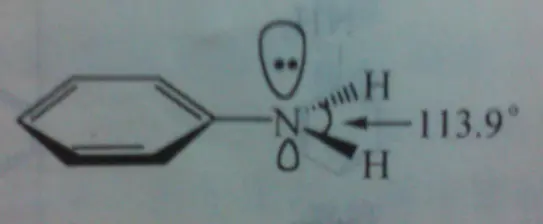
2.Aniline conjugate structure
The N [3] in aniline is nearly sp2 hybridized (actually it is still sp3 hybridized), the lone pair of electron occupied orbitals can be conjugated with benzene ring,
the electron cloud can be dispersed on the benzene ring, so that the density of electron cloud around the nitrogen is reduced.

3.Aniline use
Aniline is one of the most important intermediates in the dye industry, which can be used in the manufacture of acid ink blue G,
acid medium BS, acid soft yellow, direct orange S, direct rosé, indigo blue, disperse yellow brown, cationic rosé FG and active brilliant red X-SB, etc.;
in organic pigments, it is used in the manufacture of golden red, golden red g, big red powder, phenocyanine red, oil soluble black, etc.
In the printing and dyeing industry, it is used for the production of aniline black;
in the pesticide industry, it is used to produce many insecticides and fungicides such as DDV, weed killer, poisonous amine, etc. Aniline is an important raw material for rubber auxiliaries,
used to manufacture antioxidant A, antioxidant D, antioxidant RD and antioxidant 4010, accelerator M, 808, D and CA, etc.
It can also be used as raw material for pharmaceutical sulfa drugs, and is also an intermediate for the production of spices, plastics, varnishes, films, etc.
It can also be used as a raw material for pharmaceutical sulfa drugs, as well as an intermediate in the production of spices, plastics, varnishes, films, etc.;
and as a stabilizer in explosives, an explosion-proof agent in gasoline, and as a solvent; it can also be used to manufacture hydroquinone, 2-phenylindole, etc.
Aniline is an important raw material for the production of pesticides, from aniline can be derived N-alkyl aniline, alkyl aniline, o-nitroaniline, cyclohexylamine, etc.
It can be used as an intermediate for the fungicide sodium diquat, seed dressing, insecticide triazophos, pyridazinphos, quinpirole, herbicide alachlor, cyromazine, imidazolinic acid, etc.
4. Overview of the dangers of aniline and precautions for its use
Acute poisoning manifestations

It mainly causes methemoglobinemia and liver, kidney and skin damage.
If a large amount of aniline is absorbed into the skin or inhaled within a short period of time, methemoglobinemia appears first,
which is manifested as cyanosis, blue-brown color of tongue, lips, finger (toe) nails, cheeks and auricles, and in severe cases, lead gray color of skin and mucous membranes,
dizziness, headache, weakness, chest tightness, palpitation, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting,
and even impairment of consciousness. Methemoglobin is more than 10% and Hernz vesicles appear in the red blood cells
. Hemolytic anemia may occur about 4 days after poisoning. Toxic liver disease occurs within 2-7 days after poisoning.
In addition to the above symptoms of oral poisoning, the symptoms of gastrointestinal irritation are more obvious.
Eye contact: conjunctival keratitis may occur.
Skin contact: May cause dermatitis.
Chronic poisoning manifestations
Long-term exposure to low concentrations can cause toxic liver disease.
Health hazard: The product mainly causes methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia and liver and kidney damage.
Easily absorbed through the skin. Acute poisoning: Patients have cyanosis of lips, finger ends and auricles, headache, dizziness, nausea,
vomiting, numbness of fingers and mental trance; in severe poisoning, severe cyanosis of skin and mucous membranes, respiratory difficulties, convulsions, even coma and shock. Hemolytic jaundice,
toxic hepatitis and kidney damage appear. There may be chemical cystitis. Eye contact causes conjunctival keratitis.
Chronic toxicity: Patients show signs of neuroleptic syndrome with mild cyanosis, anemia and hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Skin contact can cause eczema.
Environmental hazards
Hazardous to the environment, can cause pollution to water bodies.
Flammable and explosive hazards
The product is flammable and toxic.
First Aid Measures
Skin contact: Remove contaminated clothing immediately and rinse skin thoroughly with soapy water and water. Seek medical attention.
EYE CONTACT: Immediately lift eyelids and flush thoroughly with plenty of running water or saline for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Inhalation: Remove from the scene to fresh air quickly. Keep airway open.
If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. If breathing stops, give immediate artificial respiration. Seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Drink sufficient warm water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention.
Fire Fighting Measures
Harmful combustion products: carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides.
Fire-fighting methods: Firefighters must wear gas masks and extinguish the fire from a safe distance, upwind.
Extinguishing agents: water, foam, carbon dioxide, sand and earth.
Spill emergency treatment
Emergency treatment: quickly evacuate people in the contaminated area of the spill to a safe area and isolate, strictly limit access.
Cut off the source of fire. It is recommended that emergency response personnel wear self-contained positive pressure respirators and gas-protective clothing.
Do not touch the spill directly. Cut off the source of the spill if possible. Prevent flow into restricted spaces such as sewers and flood drains.
Small spills: Adsorb or absorb with sand or other non-combustible materials.
Large spills: Construct dikes or dig pits to contain.

Spray aerosol water or foam to cool and dilute vapors and protect site personnel. Transfer to tanker or special collector with pump, recycle or transport to waste disposal site for disposal.
On December 31, 2012, at 7:40 pm, an aniline leak caused by a ruptured conveying hose occurred at Shanxi Tianji Coal Chemical Group Co. located in Lucheng City,
Changzhi City. The leaking aniline flowed out of the province with river water, causing a large area of water outage in Handan City.
Operation and disposal storage
Operating precautions: operate airtight and provide adequate local exhaust ventilation.
Operation is mechanized and automated as much as possible. Operators must be specially trained and strictly follow the operating procedures.
It is recommended that operators wear filtered gas masks (half masks), safety glasses, anti-toxicant penetration overalls, and rubber oil-resistant gloves.
Keep away from fire and heat sources, and smoking is strictly prohibited in the workplace. Use explosion-proof ventilation systems and equipment.
Prevent vapors from leaking into the workplace air. Avoid contact with oxidizers and acids. Handle lightly to prevent damage to packaging and containers.
Equipped with appropriate varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment and leak emergency handling equipment. Empty containers may have harmful residues.
Storage precautions: Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse.
Keep away from fire and heat sources. Storage temperature should not exceed 30℃ and relative humidity should not exceed 80%.
Keep away from light. Packaging requirements are sealed and should not be in contact with air. It should be stored separately from oxidizers, acids and edible chemicals, and should not be mixed.
Equipped with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment. The storage area should be equipped with leak emergency treatment equipment and suitable shelter materials.

 By Coco Ho
By Coco Ho