What is Polyacrylamide?
To understand what polyacrylamide is, let’s first define a polymer. A polymer is a chemical compound that is made up of many single units known as monomers.
The difference between polymers and other types of large molecules, such as sugars or proteins, is the way that the monomers are connected.
In classic examples like cellulose (which forms plant cell walls) and long chains of monomer units are joined to each other at their ends, creating what is known as a linear polymer.
However, some polymers also have nonlinear structures where individual units link up with each other within the chain.
Polyacrylamide meaning that is a polymer that contains the monomers acrylamide and hydroxy acrylate. It is a water-soluble solid that is used in the process of electrophoresis.
This is where charged particles are separated as they travel through solutions using an electric field—as well as being a component of a variety of products, such as fertilizers and drilling fluids.
Polyacrylamide’s unique structure gives it properties that make it useful in many applications. This is to imply that is used in the manufacturing of different types of products and in different fields.
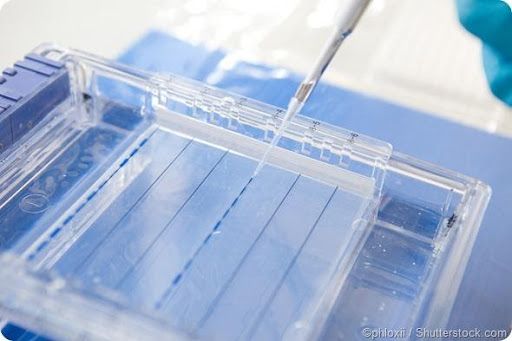
Long established in the scientific community, polyacrylamide is a versatile substance that has many uses. However, it was not until 1987 that scientists discovered how useful its structure could be for electrophoresis experiments.
Although this discovery occurred relatively recently, polyacrylamide’s unique properties have made it an essential component of many products manufactured today.
Although polyacrylamide’s chemical formula is CH2CHCONHCH2CHCONHCH(NH2)n, this single polymer has an average molecular weight of around 20 million Daltons (a unit of measurement commonly used in chemistry).
How is Polyacrylamide Formed?
Polyacrylamide’s monomer units are linked together into long chains using a process called free radical polymerization. In this process, small particles known as initiators begin the formation of each chain by initiating the addition of other monomers to the particles.
Heat (usually provided by a heat source such as a stovetop burner or hot plate) causes the initiators and monomers to form gaseous by-products such as carbon dioxide, which can be vented. The chains continue growing as long as the initiator particles are available and have monomer units attached to them.
Polyacrylamide use?
Polyacrylamide has a wide range of applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Flocculation: or thickening of wastewater (usually in water treatment plants), flocculant products contain polyacrylamide, along with other ingredients. They help remove solids from water by creating “flocks” or agglomerates of suspended particles in the liquid which then settle to the bottom of storage tanks more quickly.
- Cement: A component of some Portland cement mixtures, polyacrylamide acts as a stabilizer and can reduce gas release during hardening.
- Petroleum Drilling Fluids: Used for its ability to thicken oils used in drilling for oil shale, clean up oil spills and remove water from gels used to service oil well drilling sites, polyacrylamide helps with the production of many petroleum products.
- Explosives: Using its ability to create a porous structure when used as a thickener in gels, polyacrylamide is added to some explosives and detonator fluids so that they will be more shock-resistant.
- Molecular biology laboratories: Like acrylamide, polyacrylamide is used in molecular biology labs to separate DNA (both for purification and de-stabilization). It may also be used for packed column chromatography and restriction enzyme digests.
- Cleaning Gels: Polyacrylamide is an ingredient in many commercial cleaning gels used to clean and degrease metal, glass, and other surfaces. It helps with the removal of oil, grease, and other organic compounds from a variety of hard surfaces.
- Water Treatment: Polyacrylamide is often used as a flocculant for wastewater and in some drinking water treatment plants. It helps to remove particles from various sources before the water is returned to the source
- Food manufacturing and processing: Polyacrylamide is added to flour for loaves of bread and pastries to help gluten form strong networks that allow the dough to rise high and cook evenly.
- Cosmetics: Used as a thickener in different types of lotions, creams, and gels in cosmetic products, polyacrylamide helps these items create the right consistency and texture to let them work as intended.
- Paint thinner and cleaners: Used as an emulsion, polyacrylamide helps paints and cleaners stay evenly distributed in the water.
- Household products: Polyacrylamide flocculants can be found in a variety of household products such as puffy paint (a type of spray paint), bubble wrap, disposable diapers, and cat litter.

Polyacrylamide is a synthetic polymer made from acrylamide monomers. It has a wide range of industrial and scientific applications, including in water treatment, oil and gas production, agriculture, papermaking, and biotechnology. Here are some common uses of polyacrylamide:
- Water treatment: Polyacrylamide is used as a flocculant in water treatment to remove suspended solids, turbidity, and other contaminants. It works by forming a gel-like substance that captures particles and allows them to settle to the bottom of the water.
- Enhanced oil recovery: Polyacrylamide is used in the oil and gas industry to increase the efficiency of oil recovery by improving the flow of oil through porous rock formations.
- Agriculture: Polyacrylamide is used in agriculture as a soil conditioner and water retention agent. It can help prevent soil erosion, improve soil structure, and increase crop yields.
- Papermaking: Polyacrylamide is used in the paper industry as a retention aid to improve paper quality and reduce papermaking costs.
- Biotechnology: Polyacrylamide is used in gel electrophoresis, a common laboratory technique used to separate and analyze proteins and nucleic acids.
Overall, polyacrylamide is a versatile polymer with a wide range of applications in various industries.
Is polyacrylamide toxic?
Because of its potential to irritate the skin, eyes, and nose/lungs of those exposed to it, polyacrylamide is considered a toxin. People should avoid touching the substance and wash hands thoroughly after coming into contact with it.
Due to its potential to cause severe skin irritation, polyacrylamide should not be used as a skin lotion or other cosmetic product unless the manufacturer has specifically labeled it for that purpose.
People who work with products that contain this chemical should also wear gloves and other protective clothing at all times to avoid direct exposure.
Is polyacrylamide plastic?
Although polyacrylamide is derived from plastic, it has properties that make it different from its parent material. Owing to their unique structure, polyacrylamide’s chains do not readily absorb water and are less sticky than those of their plastic counterparts.
In fact, they are so water-repellant that the polymer is sometimes used in place of oil-based drilling fluids or muds—which can work better in dry environments.
Most plastics will dissolve when exposed to acids or bases (commonly known as corrosive chemicals).
However, because polyacrylamide has more monomer units per average molecular weight than its plastic counterparts, it does not dissolve as readily in these common solvents.
Polyacrylamide manufacturer in China
China is one of the world’s leading countries when it comes to polyacrylamide manufacturing. China is one of the few places where this material can be easily produced.
This means that commercial polyacrylamide factories can set up a process for producing it anywhere in the country on short notice.
There are several polyacrylamide manufacturers in China, some of which include:
- SNF China – a subsidiary of the SNF Group, one of the world’s largest producers of water-soluble polymers.
- Kemira China – a global chemical company that produces a range of chemicals and additives, including polyacrylamide.
- Shandong Polymer Bio-chemicals Co., Ltd – a company that specializes in the production of polyacrylamide and other water treatment chemicals.
- Xitao Polymer Co., Ltd – a company that produces various types of polyacrylamide, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic polyacrylamide.
- Gongyi City Xianke Water Supply Material Co., Ltd – a manufacturer of polyacrylamide and other water treatment chemicals.
- Suneco Chem Co., Ltd – a manufacturer of polyacrylamide and other water treatment chemicals.
It’s important to note that choosing a reliable and high-quality polyacrylamide manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and safety of its use in various applications.
Find out the polyacrylamide cost directly from the manufacturer.
To remain competitive with other polyacrylamide suppliers, China offers its clients partnerships that allow them to participate in various aspects of production from beginning to end.
So, if you are looking for polyacrylamide for use, contact reliable manufacturers in China and place your order.







