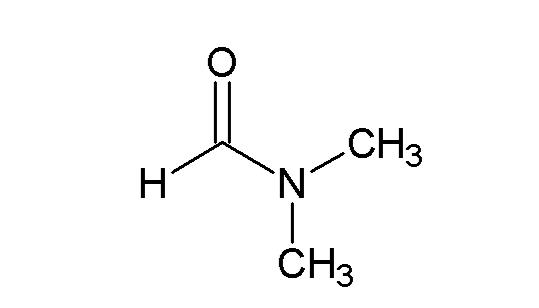
N,N-dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the molecular formula C3H7NO, which is a colorless and transparent liquid.
It is a kind of chemical material with wide application, and also a kind of excellent solvent with wide application.
It can be mixed with water and most organic solvents except halogenated hydrocarbons, and has good solvency ability for many organic and inorganic compounds.
1. Dimethylformamide properties and stability.
1. It is a non-protonic polar solvent, with good solubility for many organic and inorganic compounds, and good chemical stability in the presence of no alkali, acid and water.
2. Chemical properties: It is relatively stable in the presence of no acid, alkali and water, even when heated to boiling point.
It decomposes into formic acid and dimethylamine salt under the action of acid, and into formate and dimethylamine under the action of base.
3. Decomposed into dimethylamine and formaldehyde by the action of ultraviolet light, and decomposed into dimethylamine and carbon monoxide when heated to about 350℃.
Form a relatively stable equimolar adduct with hydrochloric acid, its melting point is 40℃, boiling point is 110℃.
With sulfur trioxide can also form crystalline adducts, its melting point is 138 ℃, boiling point is 145 ℃, DMF-SO3 can be used as a moderate sulfonation agent and sulfuric acid agent.
Phosphorus pentoxide is insoluble in N,N-dimethylformamide at room temperature, but after forming a stable complex above 40°C, it can be dissolved at room temperature without precipitation.
It reacts vigorously and emits hydrogen gas when heated in the presence of sodium metal.
It also reacts vigorously with triethylaluminum at 0℃. Also reacts with Grignard reagent.
Reacts with chloride and anhydride to produce dicarboxamide derivatives.
4. It is a low toxicity class. Animal tests have shown that continuous administration of large amounts of N,N-dimethylformamide causes weight loss and hinders hematopoietic function.
It has strong irritating effect on eyes, skin and mucous membrane, and its liquid or vapor can cause liver disorder after being absorbed by skin.

Inhalation of high concentration of vapor can cause acute poisoning, the main symptoms are severe irritation, generalized cramps, painful constipation and nausea, vomiting and so on.
In addition to skin and mucous membrane irritation, chronic poisoning also includes nausea, vomiting, chest tightness, headache, general discomfort, reduced appetite, stomach pain,
constipation, liver enlargement and changes in liver function, and an increase in urobilinogen and urobilin.
The average vapor concentration of 29.9 mg per cubic meter or less is required for use, and symptoms of poisoning (injury to the central nervous system) occur at 59.8 mg per cubic meter.
The oral toxicity LD50 of rats and mice is 3000~7000mg/kg.
olfactory threshold concentration is 0.14mg/m3, TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 10mg/m3.
5. Stability: stable

6. Prohibited substances: strong oxidizer, acyl chloride, chloroform, strong reducing agent, halogen, chlorinated hydrocarbons, concentrated sulfuric acid, fuming nitric acid.
7. Polymerization hazard: no polymerization
2. Dimethylformamide storage method
Storage precautions Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep away from fire and heat source.
Keep the container sealed. It should be stored separately from oxidizing agent, reducing agent, halogen, etc.
and should not be mixed. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. Prohibit the use of spark-prone machinery and tools.
The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency treatment equipment and suitable shelter materials.

3. Dimethylformamide synthesis method
Since the first synthesis of dimethylformamide by the reaction of formic acid and dimethylamine in 1899, the process methods of synthesizing dimethylformamide with different raw materials have been developed,
such as dimethylamine – carbon monoxide method, formamide – dimethylamine method, cyanuric acid – methanol method, acetonitrile – methanol method,
methyl formate – dimethylamine method, trichloroacetaldehyde – dimethylamine method and so on. But the current industrial production abroad is still dominated by the dimethylamine – carbon monoxide method.
1、Methyl formate-dimethylamine method: Formic acid is esterified with methanol to produce methyl formate, then reacted with dimethylamine in gas phase to produce dimethylformamide,
and then distilled to recover methanol and unreacted methyl formate, and then distilled under reduced pressure to produce finished products.

2、Dimethylamine-carbon monoxide method: It is obtained by the direct reaction of dimethylamine and carbon monoxide in the presence of sodium methanol.
Reaction conditions are 1.5-2.5MPa and 110-150℃. The crude product is produced by distillation to the finished product.
3、Methyl formate is obtained by carbonyl synthesis of carbon monoxide and methanol under high pressure and 80-100℃ temperature, then react with dimethylamine to produce dimethylformamide,
and the finished product is obtained by distillation.
4、Trichloroacetaldehyde method: obtained by the reaction between trichloroacetaldehyde and dimethylamine.
Add chloroform and 0.52 parts of trichloroacetaldehyde into the reaction kettle, cool it to below 30℃, pass in gaseous dimethylamine,
and at the same time drop its she 0.78 parts of trichloroacetaldehyde into the reaction kettle and carry out the reaction.
After the reaction is finished, distillation operation is carried out, and the fraction when the temperature at the top of the distillation tower is 58-64℃ is chloroform,
and the fraction at 64-150℃ is a mixture of chloroform and dimethylformamide,

and this mixture is distilled under reduced pressure to obtain crude dimethylformamide, and then the crude crystal is distilled again to obtain the finished product.
4.Dimethylformamide use
1. Dimethylformamide is a good solvent for a variety of polymers such as polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylonitrile, polyamide, etc.
It can be used in the wet spinning of synthetic fibers such as polyacrylonitrile fiber, polyurethane synthesis; used in plastic film making; also can be used to remove paint stripper;
it can also dissolve certain low-solubility pigments, so that the pigments with the characteristics of dyes.
Dimethylformamide is used in the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons and for the separation and recovery of butadiene from carbon IV fractions and isoprene from carbon V fractions;
it is also used as an effective reagent for the separation of non-hydrocarbon components from paraffin.
2. It has good solubility selectivity for isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid:

isophthalic acid is more soluble in dimethylformamide than terephthalic acid, and solvent extraction or partial crystallization in dimethylformamide can separate the two.
In petrochemical industry, dimethylformamide can be used as gas absorber to separate and refine gas.
3. In organic reaction, dimethylformamide is not only widely used as solvent for reaction, but also an important intermediate in organic synthesis.
In pesticide industry, it can be used to produce pesticide amitraz.
4. Non-aqueous solution titration reagent, solvent for ethylene resin and acetylene, organic synthesis, photometric determination,
gas chromatography stationary solution (maximum use temperature 50℃, solvent is methanol), separation and analysis of C2-C5 hydrocarbons,
and can separate n- and isobutene and cis- and trans-butene. Analysis of pesticide residues.
Organic synthesis. Peptide synthesis. Photographic industry.
5. An excellent solvent and chemical raw material with wide application. It is an excellent solvent for many polymers such as polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylonitrile, polyamide, etc.
It can be used in wet spinning of synthetic fibers such as polyacrylonitrile fiber; synthesis of polyurethane;
paint stripper for paint removal; selective absorption of acetylene and separation and refinement of butadiene; used as solvent in the production of artificial leather;
used in the synthesis of pesticides; used in the synthesis of iodamidopyrimidine, doxycycline, cortisone, vitamin B6, iodoside, repellent pinch, thiazine,
N-formyl sarcoma lysate, antitumor It is used in the synthesis of iopamidopyrimidine, doxycycline, cortisone, vitamin B6, iodoside, repellent pin, thiazine,

N-formyl lysosarcoma, antitumor, methoxylated aromatic mustard, bianzale, cyclohexylnitrosourea, furofluorouracil, hemostatic cyclic acid, betamethasone, megestrol, cholestyramine, paracetamol etc.
6. Used as solvent and organic modifier in liquid chromatography, extractant and unfolding agent for thin layer chromatography,
solvent for vinyl resin and acetylene, and solvent for titration of non-aqueous solvent. And used in organic synthesis.
7. Mainly used as industrial solvent, used in the pharmaceutical industry for the production, hormones, also used in the manufacture of insecticide.

 By Coco Ho
By Coco Ho



