Melamine, commonly known as dense amine, protein essence, molecular formula C3H6N6, IUPAC named “1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine”, is a triazine nitrogenous heterocyclic organic compounds, used as chemical raw materials.
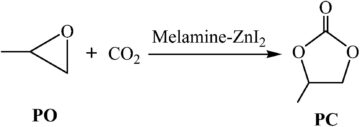
It is white monoclinic crystal, almost tasteless, slightly soluble in water (3.1g/L room temperature), soluble in methanol, formaldehyde, acetic acid, hot ethylene glycol, glycerol, pyridine, etc.,
insoluble in acetone, ether, harmful to health, and not to be used in food processing or food additives.
On October 27, 2017, the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer published a preliminary list of carcinogens for reference,
melamine is in the list of carcinogens in category 2B.

1.Physical and chemical properties of melamine
Solubility: insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethylene glycol, glycerol, ethanol, insoluble in ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride Chemical properties
2. Chemical properties of melamine
Non-combustible, stable at room temperature.
Aqueous solution is weakly alkaline (pH=8), and can form melamine salt with hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, etc.
Under neutral or slightly alkaline condition, it condenses with formaldehyde to form various hydroxymethyl melamine, but under slightly acidic condition (pH=5.5~6.5),
it condenses with derivatives of hydroxymethyl to produce resin. When hydrolyzed with strong acid or strong alkali aqueous solution, the amine group is gradually replaced by hydroxyl group,
and Mr. melamine is formed into melamine diamide, and further hydrolyzed to form melamine monoamide, and finally melamine is formed.
3. Melamine market development
Melamine is made from urea, and it takes about 3 tons of urea to produce 1 ton of melamine. China is the world’s largest producer of urea, with large urea production and low prices.
Even with the high tariffs imposed by the state to curb urea exports, the annual urea exports still amount to (3-7) million tons,
and the abundant urea resources make China’s melamine production uniquely advantageous.

The serious expansion of melamine production capacity in China has led to fierce competition among Chinese melamine enterprises and weak price increase in the industry.
4. Main uses of melamine
(1) Decorative panels: It can be made into fireproof, shock-resistant and heat-resistant laminates, brightly colored, sturdy and heat-resistant decorative panels,
veneer panels for aircraft, ships and furniture, and fireproof, shock-resistant and heat-resistant decorative materials for houses.
(2) Coating: After etherification with butanol and methanol, it can be used as high grade thermosetting coating,
gluing agent of solid powder coating, metal coating and high grade amino resin decorative paint for vehicles and electrical appliances.

(3) Molding powder: After mixing and granulating, it can be made into honey amine plastic, which is free of degree, stain resistant and can still maintain good electrical properties when wet,
and can be made into white, drop-resistant daily utensils, sanitary ware and imitation porcelain tableware, electrical equipment and other high-grade insulating materials.
(4) paper: etherification with ether can be used as a paper treatment agent to produce wrinkle-resistant, shrinkage-resistant, non-decaying banknotes and military maps and other high-grade paper.
(5) melamine formaldehyde tree ester mixed with other raw materials, can also produce fabric finishing agent, leather tanning agent, varnish and anti-water agent, rubber adhesive,
combustion aid, efficient cement water reducing agent, steel desalination agent, etc.
5. Notes on melamine
Nature of hazard

Health hazard: No occupational poisoning has been reported. Note that the product can decompose under high temperature to produce highly toxic cyanide gas.
Flammability hazard: The product is non-flammable.
First Aid Measures
Skin contact: Remove contaminated clothing and flush with plenty of running water.
Eye contact: Lift eyelids and flush with running water or saline. Seek medical attention.
Inhalation: Remove from the scene to fresh air. Seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Drink sufficient warm water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention.
Fire-fighting measures
Hazardous characteristics: Decomposition by heat emits highly toxic cyanide gas.
Harmful combustion products: carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrogen cyanide.
Fire-fighting methods: Firefighters must wear filtered gas masks (full face shield) or isolated respirators, full-body fireproof gas-proof clothing,
and extinguish the fire upwind. Move the container from the fire to an open area if possible.
Spill handling

Emergency response: isolate the contaminated area of the spill and restrict access. Recommend that emergency response personnel wear dust masks (full face shields) and hazmat suits.
Collect in dry, clean, covered containers with clean shovels and move to a safe place. If a large amount is leaked, collect and recycle or transport to waste disposal sites for disposal.
Operation and disposal
Operating precautions: Airtight operation with full exhaust. Operators must be specially trained and strictly follow the operating procedures.
It is recommended that operators wear self-absorbing filtered dust masks, chemical safety glasses, anti-toxicant penetration overalls and rubber gloves.
Avoid dust generation. Avoid contact with oxidizers and acids. Handle lightly to prevent damage to packaging and containers.
Equipped with leak emergency handling equipment. Empty containers may have residual harmful substances.
Storage precautions: Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse.

Keep away from fire and heat sources. It should be stored separately from oxidizers and acids, and should not be mixed.
The storage area should be equipped with suitable materials to shelter spills.
5. Melamine International Standard
International Standards
On July 2, 2012, the 35th Session of the International Codex Alimentarius Commission reviewed and adopted the limit of melamine in liquid infant formula, specifically:
0.15mg/kg of melamine in liquid infant formula.
On July 5, 2012, the International Codex Alimentarius Commission, the United Nations body responsible for setting food safety standards, set a new standard for melamine in milk,
which should not exceed 0.15 mg per kilogram of liquid milk.
The Codex Alimentarius Commission said the new standard for melamine content will help governments better protect consumer rights and health.

 By Coco Ho
By Coco Ho



